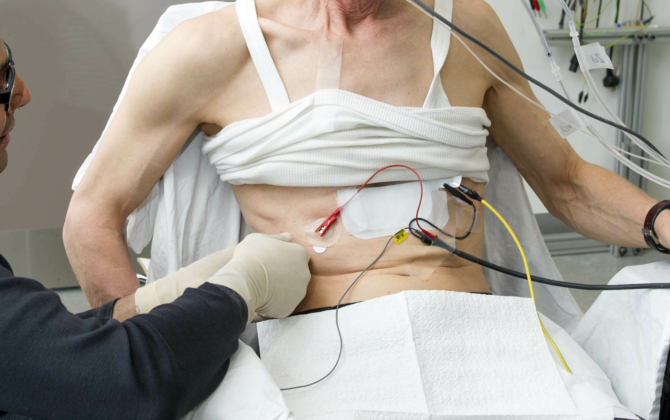
Our recent studies of the control of breathing muscles have shown a strong link between neural drive and mechanical action of the muscle. We showed that for a number of breathing muscles, the neural drive is directed to the muscles with the best mechanical effect for breathing. We termed this link between mechanics and neural drive ‘neuromechanical matching’. It is a new principle of muscle activation that allows for metabolically efficient activation of the muscles. This basic research finding is now leading to further studies in patients with respiratory disorders where muscle mechanics have changed. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is one such disease, where muscle mechanics are known to change. Our new studies will look at whether these patients have “adapted” to the changed muscle mechanics or whether their muscles may be activated inefficiently.
About
News & Publications
Search
Your Health
Our Research
Resources & Tools
Menu